Gallery
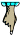
|
|

American Gothic
Grant Wood, 1930
|
|

Radiovisor gave blurry
orange TV picture, 1930
|
|

Scotch Tape
1931
|
|

Persistence of Memory
Salvador Dali, 1931
|
|

IBM Radiotype
1931
|
|

Felix the Cat TV image>
broadcast by RCA
1931
|
|

35 mm reflex camera
Germany, 1933
|

Nazi book burning
1933
|

King Kong
1933
|

Salvador Dali's
Mae West, 1934
|

Mechanical TV
30 line scan, 1936 |
|

Piet Mondrian's
Opposition of Lines,
Red and Yellow,
1937 |
|

George Stibitz' Model K
calculator, 1937
|

Paul Klee's
Picture Album, 1937 |
|

René Magritte's
Time Transfixed, 1938
|

Wire recorder
invented in 1939
|

